Geosensor networks
Geosensor Networks (GSN) – real-time monitoring (Real-Time: RT) and near Real-Time: NRT natural changes: acquisition, processing and modeling of geospatial data

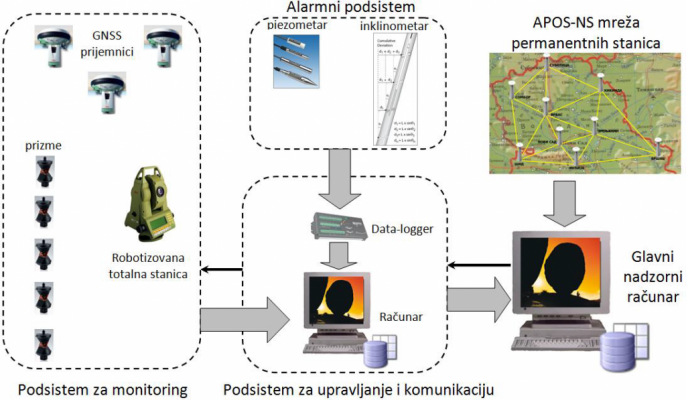
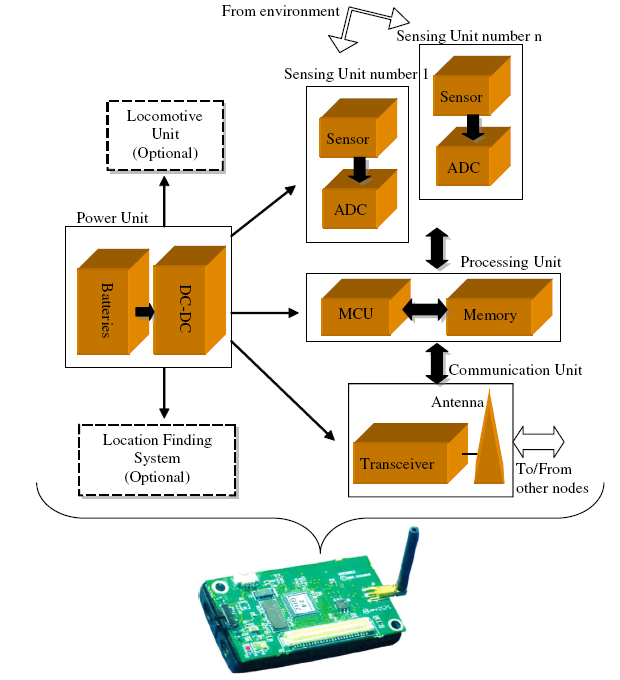
GSN STRUCTURE – The basic elements of the GSN are individual multifunctional sensory nodes (Sensor Nodes). Sensor nodes connect to the communication network, thus forming a geosensor network.
CLASSIFICATION OF TYPES OF GEOSENZOR NETWORKS
According to the mobility of knots
- Static (nodes are immobile)
- Dynamic (moving nodes)
According to the mode of communication
- Wired Sensor Networks, direct power supply
- Wireless (Wireless Sensor Networks – WSN, battery power)
By way of control
- Centralized management (wired SN)
- Decentralized Management (WSN)
According to the localization of knots
- without known node coordinates
- with known node coordinates
CLASSIFICATION OF GEOSENZOR NETWORK TASKS – Types of natural phenomena that are monitored by geosensor networks in RT and / or NRT: OBJECTS AND FIELDS
- Spatial-weather monitoring of MOBILE FACILITIES (more individual or in group)
2. Spatial-Time Tracking FIELD (event is within the network)
3. Spatial-Weather Tracking IVICA (the event is partially online)
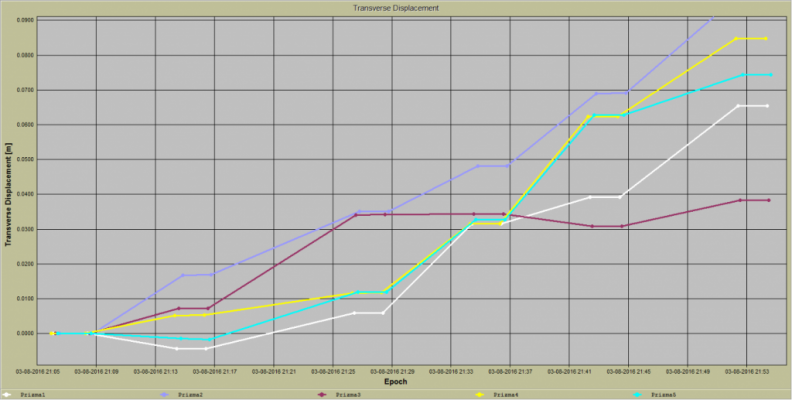
4. GSN – GEOMATIC APPLICATION – Real-Time (RT) and Near Real-Time (NRT) MONITORING DEFORMATION
- Monitoring deformation involves monitoring the dimensions and positions of objects and / or terrain and is one of the standard tasks of geodesy
- The extension of standard (periodic) monitoring of deformation to deformation monitoring in real (RT) and near real time (NRT) is ensured by the application of GSN – the standard task GEOMATIKA
- Deformation is a change in the shape of the object (stretching, compaction, or other type of shape change) and / or its position, as well as changing the position and / or structure of the site. It is most often caused by the effect of some kind of strain, but can be caused by changing the temperature and humidity of the environment
Application of GSN for monitoring deformation
- Objects: BRIDGES, BRANDS, BUILDINGS, TUNNELS (jacket) … Terrain: SIDES, NATURES, OPEN BATHS, TUNNELS (land) …
MODERN TECHNOLOGIES FOR RT / NRT MONITORING DEFORMATION
GEODETIC SENSORS
- GNSS devices
- Robotized total cells
- Digital Levels
- Laser scanners
GEOTECHNICAL AND OTHER SENSORS
- inclinometers
- piezometers
- sensors of force
- accelerometers
- extensometers
- cameras
- air / water / soil sensors
- meteo sensors …
COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES
- Wireless communication
- Web technologies
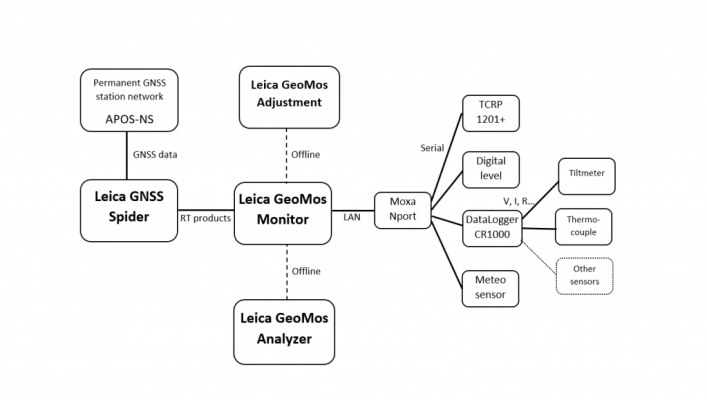
EQUIPMENT AND SOFTWARE
The Geoinformatics Laboratory possesses the following devices and data acquisition software in the framework of the analysis of the work of geosensor networks
Sensors – HARDVER
- Network of permanent stations APOS-NS (Territory of AP Vojvodina, 9 receivers)
- Robotized total cell
- Digital Level
- Terrestrial laser scanner
- GNSS devices
- Tiltmeter
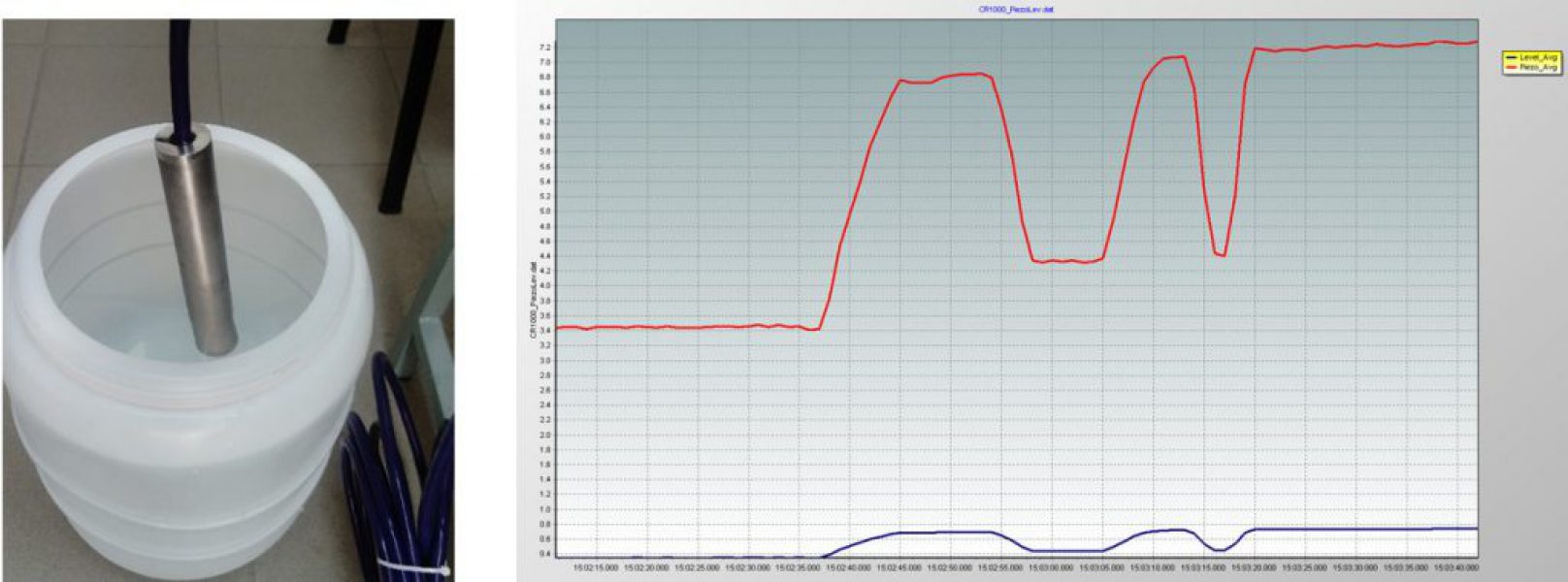
- Piezometer
- Force sensors
- Two-axis accelerometers
- Craft encoder (incremental)
- Thermopar N type
- Weather sensor (temperature and pressure)
Monitoring deformations in RT / NRT – SOFTWARE
- Licensed software: Leica GeoMos
- Software for Data Logger programming
- Development of own modules for analysis and processing
Communication
- Data logger
- COM server
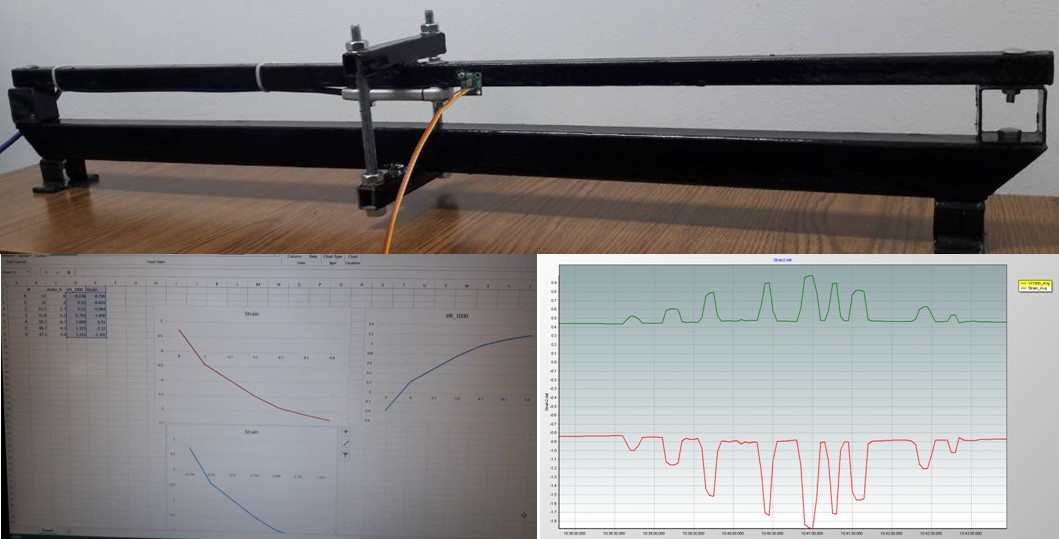
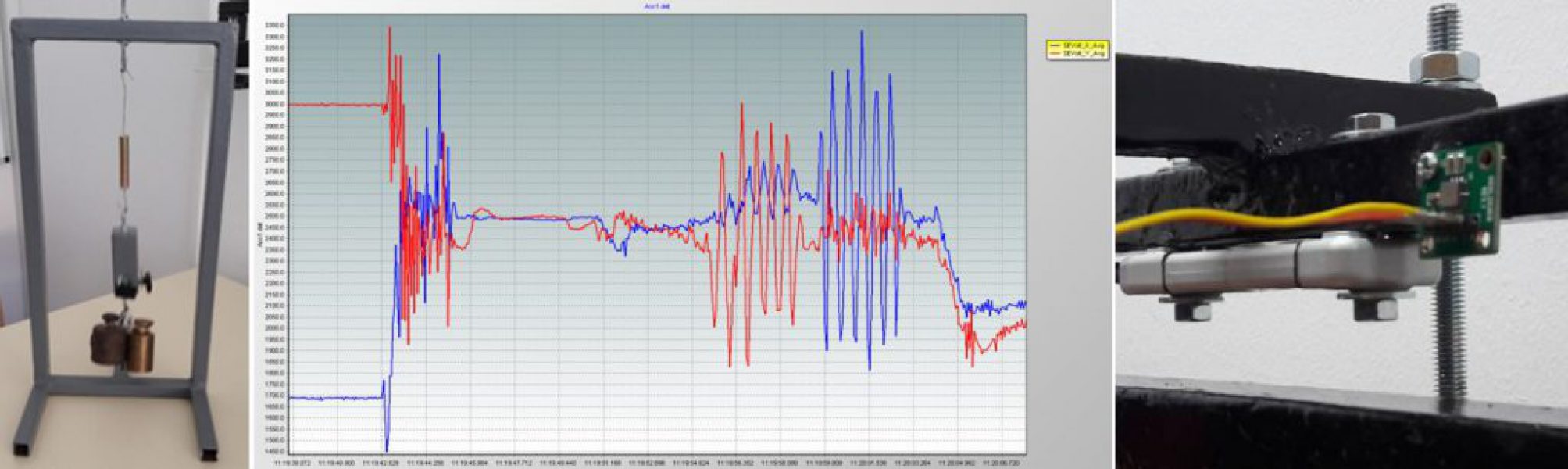
Measuring the vibrations caused by the stresses of the structures using the accelerometer.
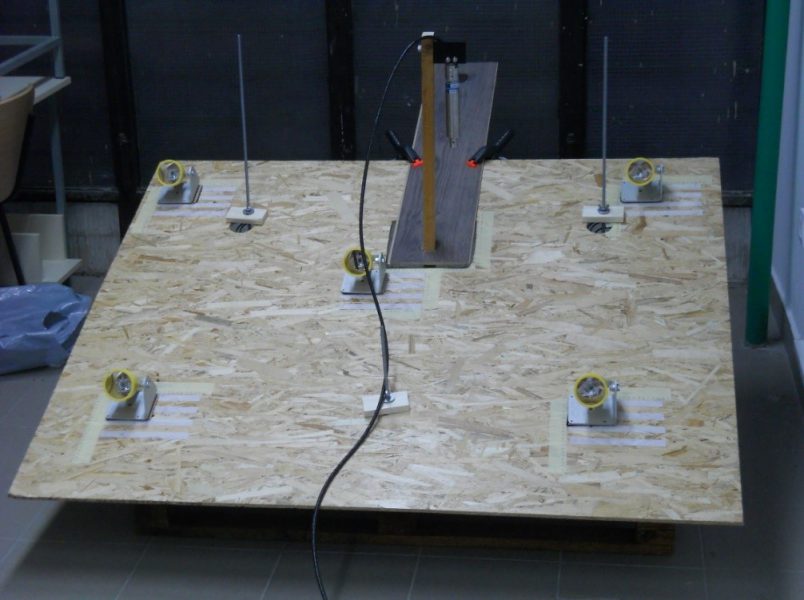
7.2. Monitoring of RT / NRT changes in the land structure (landslides, embankments, open mines)
Physical landslide model
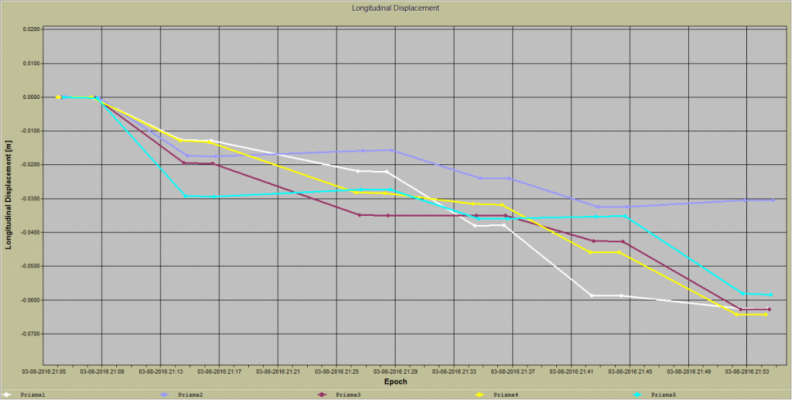
Measurements of longitudinal and transverse movements using a robotized total cell
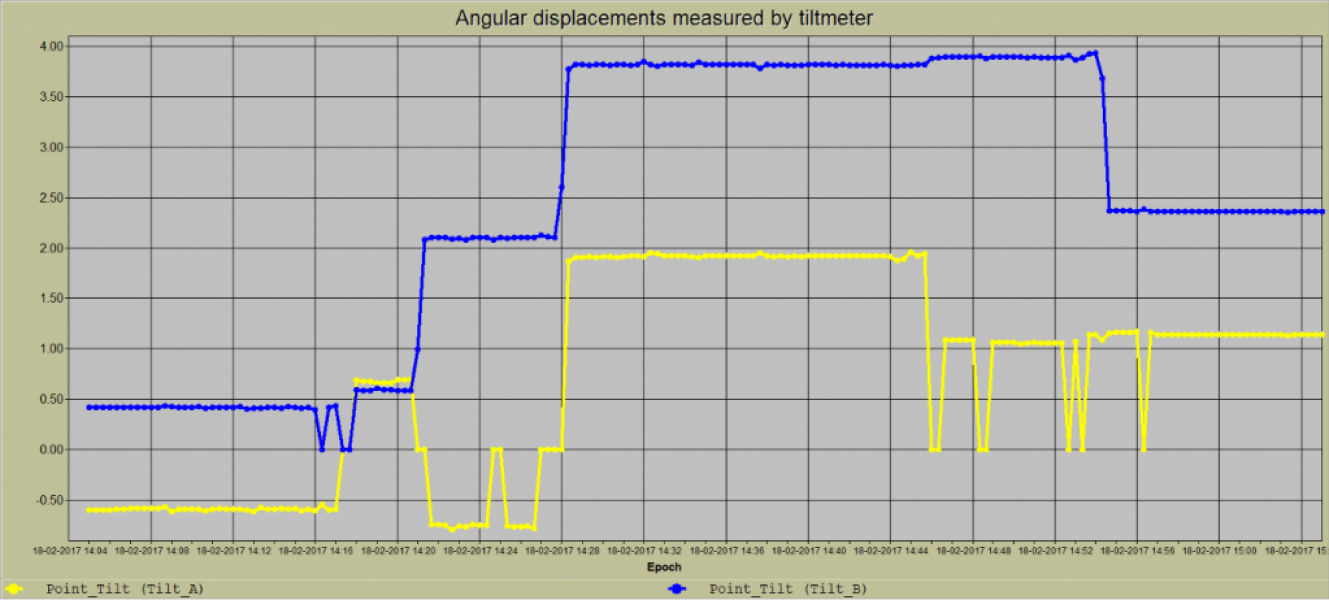
Measurement of counter-movements using tiltmeter
Measurement of groundwater level with piezometer