GNSS and LOCATION-BASED SERVICES
Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) are satellites in orbit around the Earth where satellites are used as reference points for positioning.
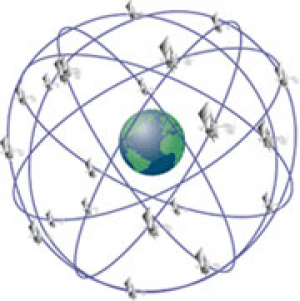
There are four GNSSs (different levels of functionality), along with some others that are under development or are planning their development. Active Systems:
- NAVSTAR GPS
- GLONASS
- Compass (BeiDou2)
- Galileo
GNSS systems consist of three segments:
- Space – made up of satellites and signals emitted by these satellites. The satellite’s orbit is about 20000km from the Earth’s surface.
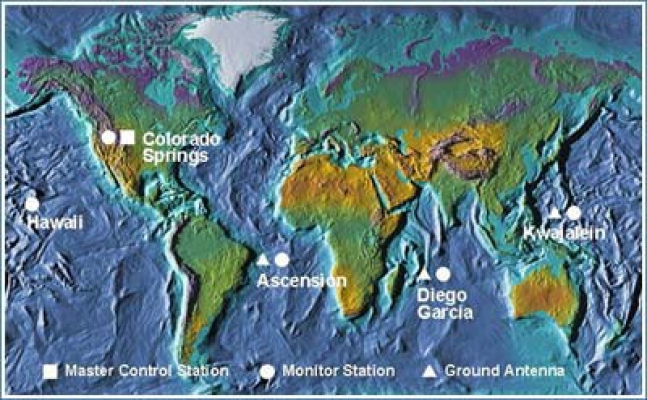
2. Control – stations on Earth that monitor the operation of satellites and calculate necessary corrections and additional parameters.
3. User-GNSS receivers, i.e. all devices that use the signal from the satellite.
GNSS systems allow positioning anywhere on the Earth’s surface, if there are no obstacles for receiving signals with at least 4 satellites at the same time. The accuracy of the positioning depends on the measurement conditions, but the accuracy of the order of the meter is most often achieved. By applying advanced measurement techniques it is possible to achieve the accuracy of the order of centimeters, and in the long periods of observation and sub-centimeter accuracy.
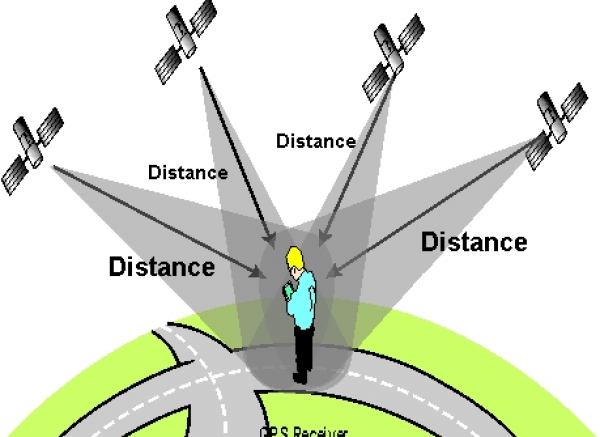
In most cases, the use of a network of permanent GNSS stations is used to increase accuracy. It is a network of connected GNSS receivers that forward data to the central server. Server based on the observation of correction bill stations that are forwarded to GNSS devices that are in the field in diameter. The accuracy of this way of positioning is 2-5cm, while keeping it at a point is only a few seconds.
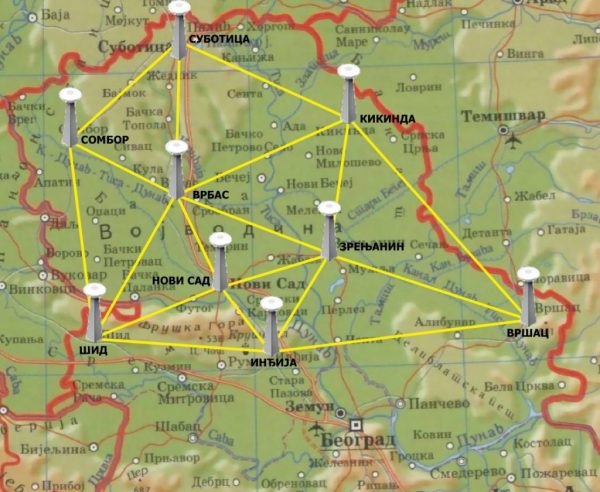
APOS-NS (Academic Positioning System) is a network of permanent stations managed by the Faculty of Technical Sciences. It consists of 7 stations, with two more are planned. The network is based on the VRS concept (Virtual Reference Station), which enables the accuracy of positioning from 2 to 5cm, in the short initialization time.
The application of the GNSS system is extremely wide and includes various activities:
- Navigation in passenger and commercial vehicles
- Vehicle Tracking and ITS (Intelligent Transportation Systems) Maritime traffic Air traffic
- Navigation in agricultural machines and precision farming (Precise farming)
- Navigating and managing construction machines
- Geodetic diameter
- Engineering geodesy
- Monitoring deformation of terrain (landslides, landslides …) and objects (bridges, dams …)
- Geological, geodynamic, seismological, volcanological research
- Aerial Photographic Recording and Laser Scanning from the Air (Airborne LIDAR)
- Biology research
- Biomedical applications .