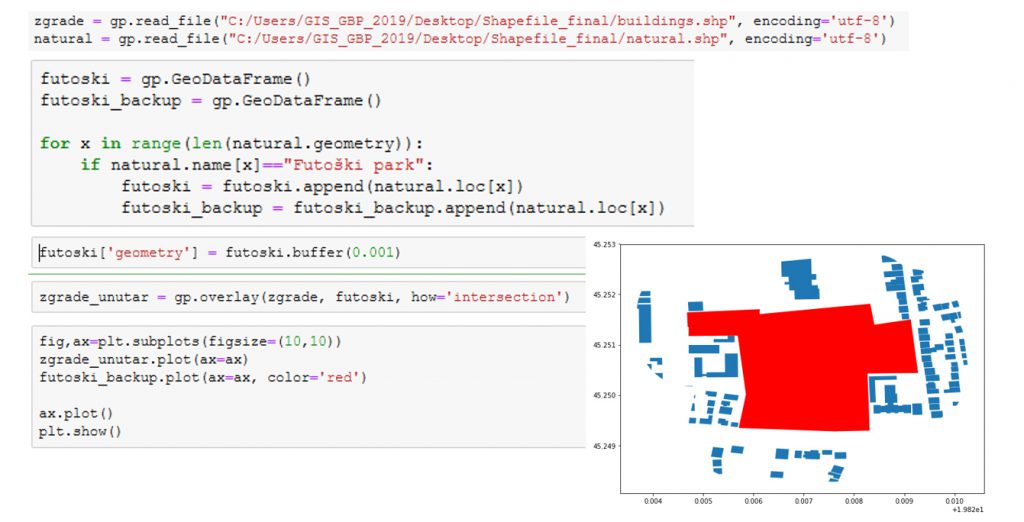
Geographic information systems
Geographic information system is a system designed to obtain, store, manipulate, analize and display spatial or geographical information. GIS applications are tools that allow users to write interactive queries, analyze spatial information, change map data and display results of all these operations. GIS are specialized systems that follow not only phenomena, activities or happenings but where those phenomena, activities and happenings take place. This way geographical location becomes important attribute of activities, managing, strategies, plans and decisions.
Data that belong to the same theme are organized within layers (hydrography, objects, infrastructure, …). Each layer can contain geometric and alphanumeric information. By combining different layers, data are combined in order to get desired information.
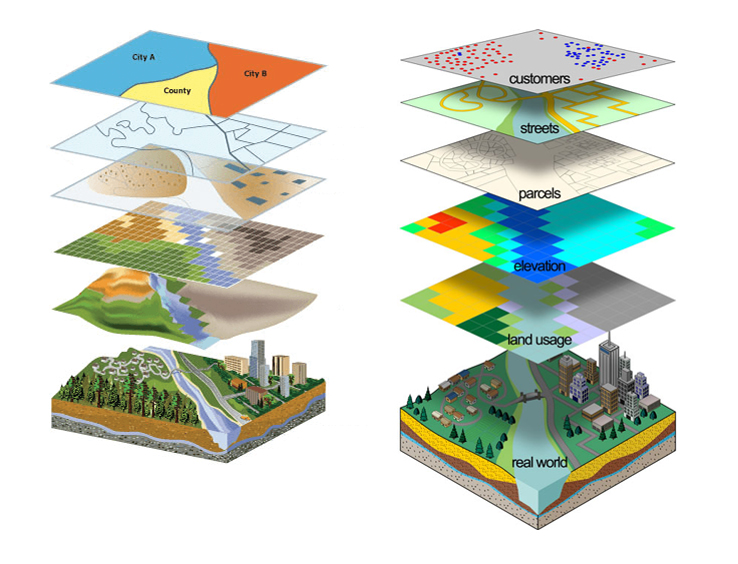
GIS can answer the following questions:
- Where are the parcels with the area between 5 and 10 acres within 10km from the highway?
- Where are the pipeline larger than 0.5m in diameter installed before 1970?
- Who are the owners of properties in certain municipality, ordered by descending values?
Maps are connected to the alphanumerical data tables. That way, the answers to former questions can be obtained trough maps, or databases. GIS considers locations of the objects when giving the answers.
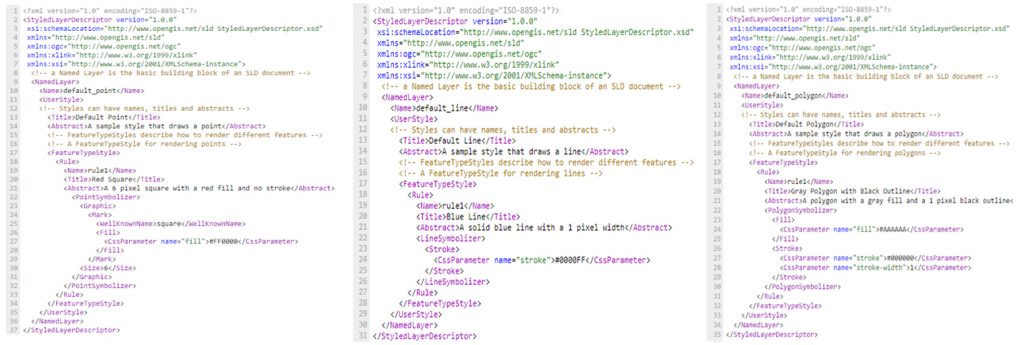
Spatial data do not have internal component that defines their visual identity. In order to display the data, they have to be styled. Styling decides the color, weight and other visual attributes that are used to portray data on maps. At Geoserver, styling is achieved trough Markup language named Style Layer Descriptor, or SLD. SLD is powerful and at some level complex XML based language. Styling is defined trough XML SLD documents. Style documents are connected to the layers at Geoserver and they define how those layers will be portrayed. One document can define the appearance of one layer. Every style has defined one or more rules that control how the style will be applied based on attributes and scale. Rules use filters that are practically logical conditions that contain expressions and functions.
Certain spatial analysis can be done trough Python. Python is a high level programming language. It supports procedural, object and functional programming. Syntax of the language allows writing of very customizable programs. Programs written in Python are most often interpreted, and large library of modules is usually provided with the interpreter. Large number of modules that allow efficient working in vast amount of areas (statistics, machine learning, spatial data, …).
GeoPandas is an open source project that makes working with spatial data in Python much easier. GeoPandas inherits datatypes that are defined in Pandas module and allow spatial datatypes operations. Geometric operations are done trough Shapely module. GeoPandas also depends on Fiona module, and Descartes and Matplotlib. The aim of GeoPandas is making spatial data operations easier. GeoPandas allows performing spatial analysis that would require spatial databases.